Facilities
We aim to develop state-of-the-art research facility for Undergraduate students of Ashoka University. The available facilities are listed below. We are expecting many more instrumental facilities very soon.
-

-
UG Lab with Chemical Fume hood
-

-
UG Lab with Chemical Fume hood
-

-
Chemistry lab student’s desk
-

-
Chemistry lab fume hood with stirrer and filtration funnel
-

-
Facility of Multi stirrer magnetic plate
-

-
Digital Melting point apparatus (upto 350 oC)
-

-
Probe Sonicator
-

-
Bacteria culture hood
-

-
Mammalian culture incubator
-

-
Mammalian biosafety hood
-

-
FPLC
-

-
Flash chromatography
-

-
Rota vapour
-

-
Bacterial culture incubator
Melting Point Apparatus measures the melting point of a substance i.e. the temperature at which the state of the substance changes from solid to liquid. The actual melting point is an indication of the purity of a substance and hence an ideal tool for the quality control of medicines, perfumes, dyestuff and other organic crystalline substances.
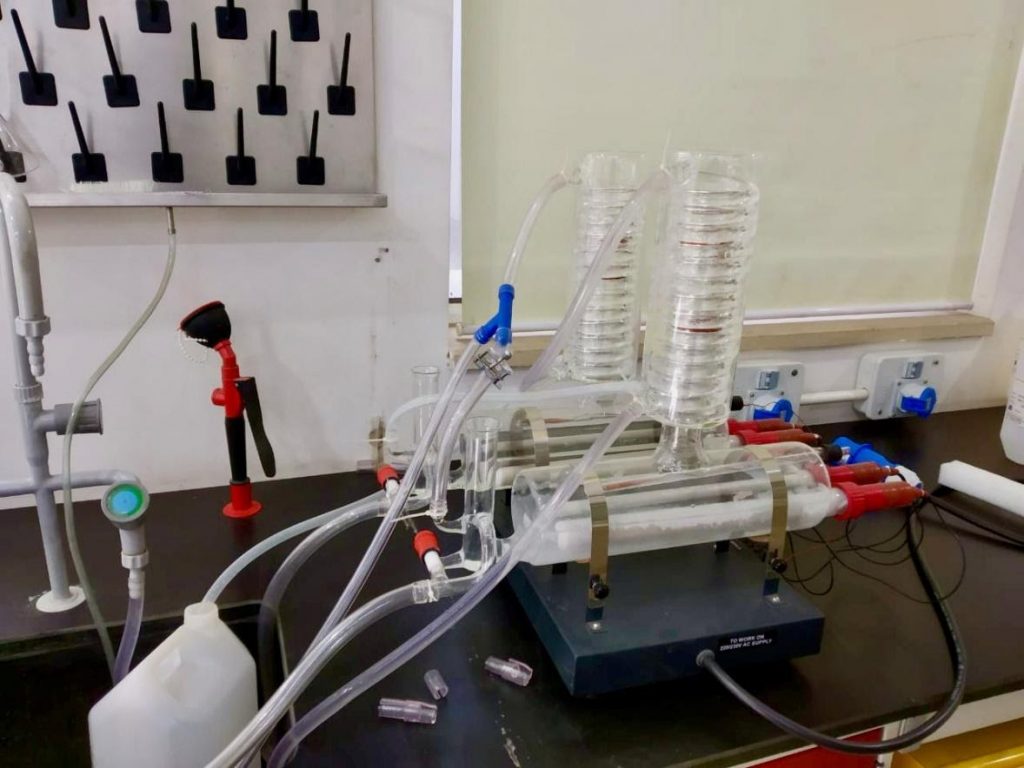
Double distillation water set-up
Double Glass Distillation Unit consists of flak with heating elements which has been embedded in fine glass. This Double Glass Distillation Unit is fused in spiral type coil fitted internally in the bottom along with tapered round glass. This is a distiller for producing distilled water for laboratory research. This set up is kept in UG Lab no. 105
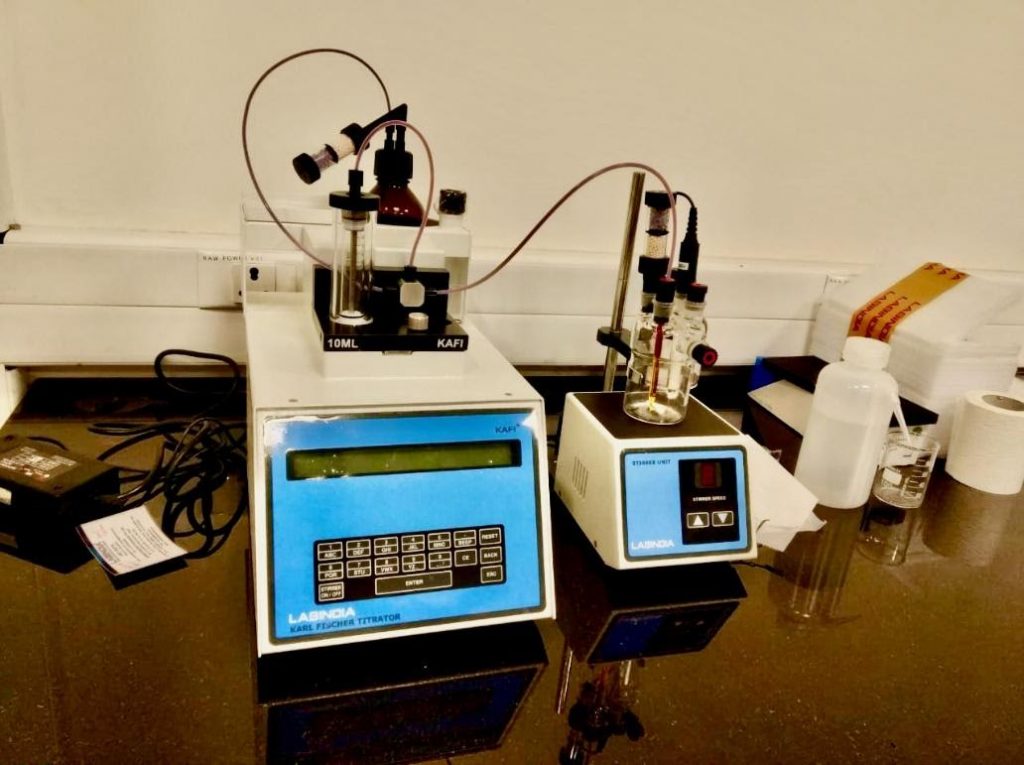
Karl Fischer titrator
arl Fischer titration is a classic titration method in chemical analysis that uses coulometric or volumetric titration to determine trace amounts of water in a sample. The elementary reaction responsible for water quantification in the Karl Fischer titration is oxidation of sulfur dioxide with iodine:
H2O + SO2 + I2 → SO3 + 2HI
This elementary reaction consumes exactly one molar equivalent of water vs. iodine. Iodine is added to the solution until it is present in excess, marking the end point of the titration, which can be detected by potentiometry. The reaction is run in an alcohol solution containing a base, which consume the sulfur trioxide and hydroiodic acid produced

Rota vapor with chiller (-20 oC) and high vacuum pump
The rotary evaporator or “rotavap” is the most efficient and most environmentally friendly way of removing a volatile solvent from a non-volatile sample.The rotovap works by increasing the rate of evaporation of the solvent by (1) reducing the pressure by attached high-vacuum pump to lower the solvent boiling point, (2) rotating the sample to increase the effective surface area and (3) heating the solution
A -20 oC chiller is attached with the rotavap,
A chiller works on the principle of vapor compression or vapor absorption. Chillers provide a continuous flow of coolant to the rotavapor cold side of a process water system at a desired temperature of about upto -20 oC. The low boiling solvent instead of exposed to air will collect in a particular vessel attached to the rotavap.
-

-
Magnetic stirrer with hotplate
-

-
Precision balance
Precision balances usually have a higher capacity than analytical balances do and typically deliver results of 0.1g, 0.01g or 1mg. These balance have finer readability, are much more sensitive to changes, and can detect smaller variations in mass
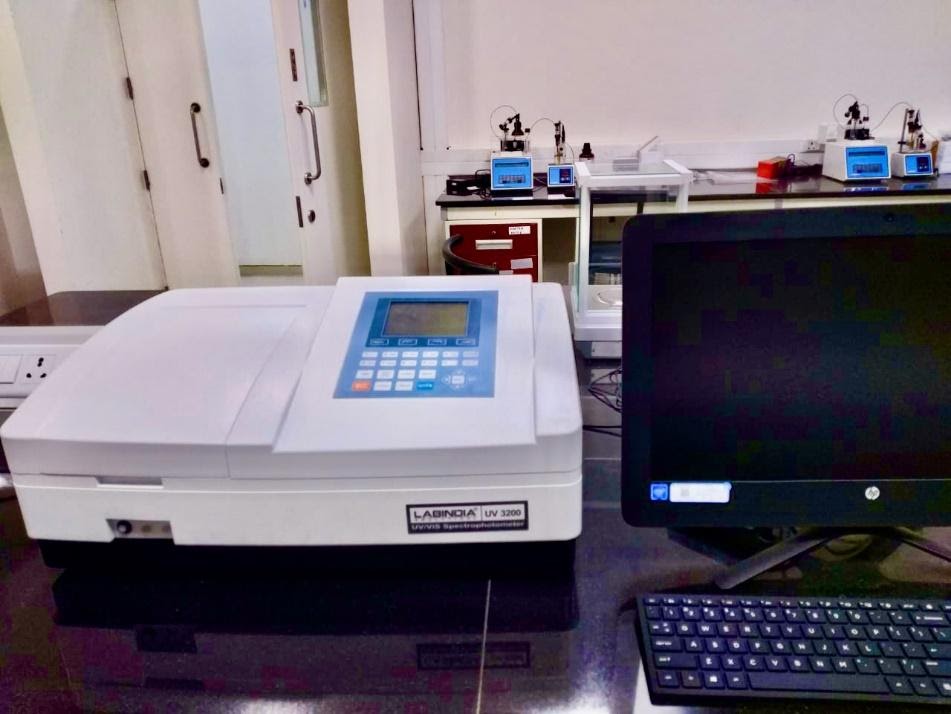

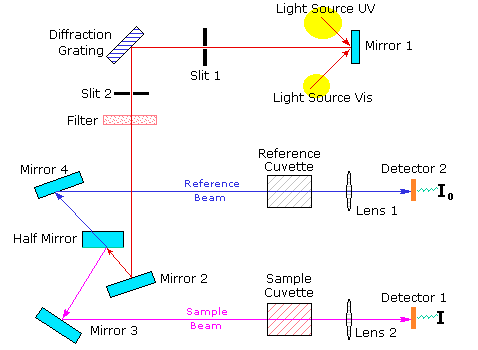
UV-vis (Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy) instrument with kinetic facility
UV-Vis spectroscopy is an absorption spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. It absorbs light in the visible, near-UV and near-infrared (NIR) ranges. This instrument is very much effective for quantitative determination of concentrations of many molecules including transition metal ions, conjugated organic compounds. The UV-Vis Spectrophotometer (Lab India 3200) was newly fitted in our UG Lab number 107. This instrument is built-up with kinetic study facility. Which means that we can study the rate of a reaction
According to Beer-Lambert law, the absorbance of a solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the absorbing species in the solution and the path length. For a fixed path length, UV/Vis spectroscopy can be used to determine the concentration of the absorber in a solution. With change of concentration the absorbance will also change.(Figure 2)
-
-
-
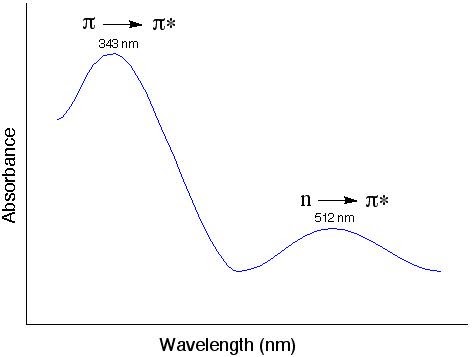
The UV-vis spectrum of tetraphenyclopentadienone
The “n” electrons (or the nonbonding electrons) are the ones located on the oxygen of the carbonyl group of tetraphenyclopentadienone. Thus, the n to π* transition corresponds to the excitation of an electron from one of the unshared pair to the π* orbital
-

-
High temperature (150 oC) dry oven
We are building up new High performance computational (HPC) facility which is under process.
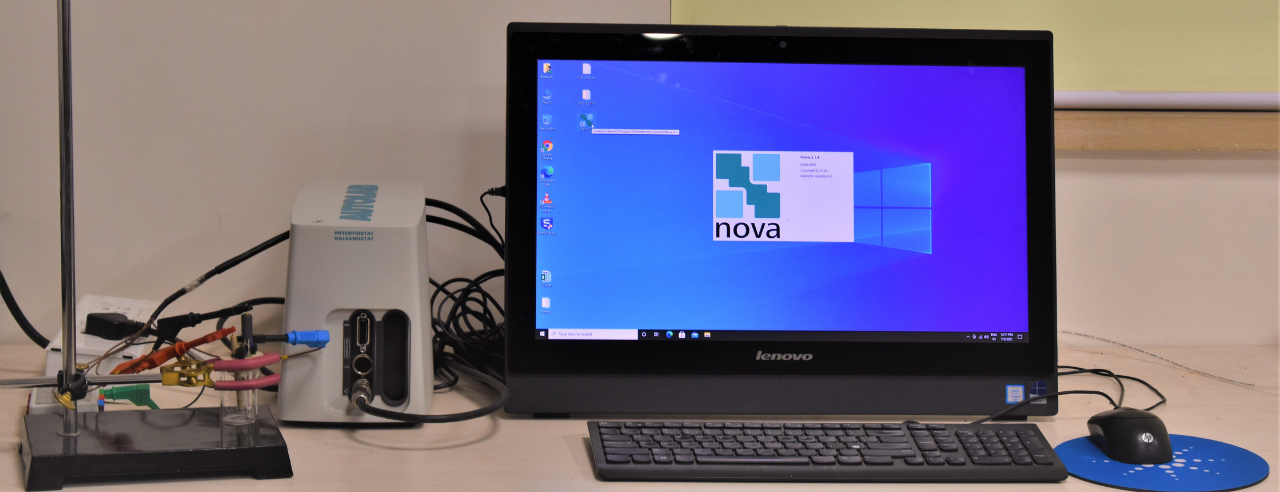
Potentiostat Spectroscopy
A Potentiostat regulates the voltage difference between two electrodes, working electrode and reference electrode in an electrochemical cell. There is a third electrode, auxiliary or counter electrode through which potentiostat controls the current. It measures the current flow between the Working and Counter electrodes.
We have potentiostat/galvanostat Autolab Metrohm PGSTAT 204N with a compliance voltage of 20V and a bandwidth of 1MHz, a maximum current of 400 mA or 10 A in combination with the BOOSTER10A.
Application
- Electrocatalyst material testing
- Mechanistic information: detection of intermediates via collection and shielding experiments (RRDE)
- Electrochemical kinetics studies
- Mass-transport properties with forced convection condition

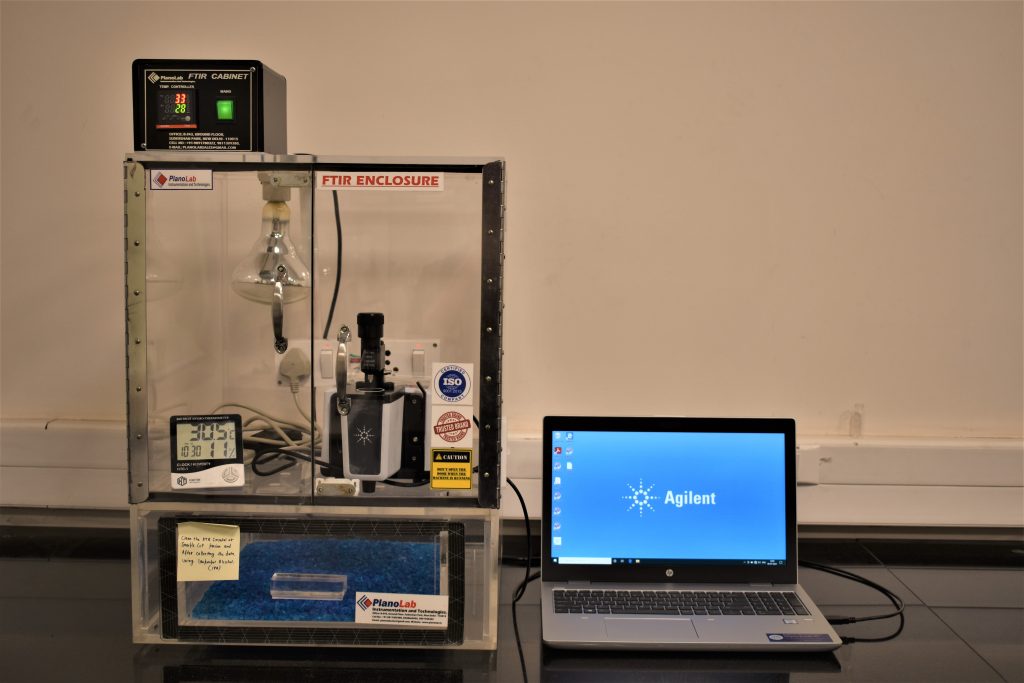
Fourier-transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
FTIR spectroscopy, is an analytical technique generally use to identify organic, polymeric, and inorganic materials. It is the third-generation Infrared spectroscopy (IR). IR spectrum is molecular vibrational spectrum. Molecules selectively absorb radiation of specific wavelength when exposed to IR radiation. Because of this, a change of dipole moment occurs which causes a transfer of electrons from ground state to excited state in its vibrational level. The intensity of IR depends on change of dipole moment and the number of absorption peak depends on vibrational energy gap. Most of the molecule are responsive to the IR, except homonuclear diatomic molecules as O2, N2 etc. The new generation FTIR has many advantages over IR (1) signal-to-noise ratio (2) accuracy (3) scan time (4) resolution of spectra and (5) scan range.
We have Agilent Cary 630 FTIR in our laboratory for measuring liquid and solid samples. Also, we have KBr hydraulic press for mainly UG students.

Schlenk Line
Some of our reactions, chemicals are sensitive to moisture and air. For this, our fume hoods are equipped with Schlenk line to carry inert condition reactions.
































